Overall, for all children and teenagers (ages 0 to 19 years) in the United States, the three most common types of cancer are childhood cancers, which are common in boys; cancer of the lung or chest for men; and cancer of the bone, skin, or gastrointestinal tract for women. Among teens, the three most common types of cancer are cancer of the bone, skin, and gastrointestinal system for boys; cancer of the colon or rectum for girls; and cancer of the breast for both boys and girls. Although most adolescent cancers are not malignant, they do occur in one out of every five cases, and they continue to affect children well into adulthood. Since most of these types of cancer are not malignant, they do not lead to death, but they still cause discomfort and pain and can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. Each type of cancer has different ways of spreading, but they usually begin in the bones, skin, or gastrointestinal system.
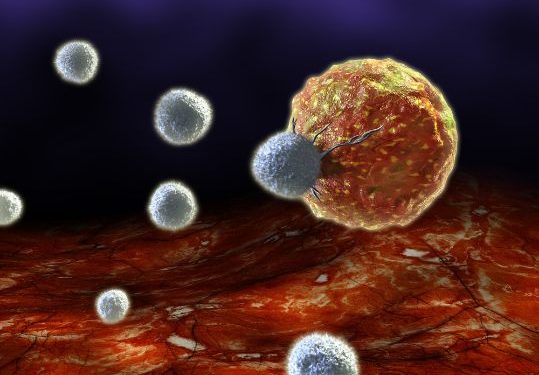
Leukemia is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among children in the United States. Leukemia occurs when the body develops antibodies that attack the blood cells. Children who have been diagnosed with leukemia need extensive treatment before they can survive. There are three types of childhood leukemia; acute, chronic, and lymphomas.
Acute cancers begin quickly and are known as “acute.” They often cause very serious symptoms and death can result quickly. Chronic types of cancer, such as lymphomas and colon and rectum cancers, are known as “chronic.” These cancers often take longer to develop and spread, and they may never exhibit signs or symptoms.
The most deadly cancers occur in women, particularly those in their reproductive years. Women are the largest organ in the body and they are at the highest risk for developing any cancer. Statistically, the risk of developing breast cancer while a woman is still a child is two times greater than that of a woman who has never had a child. For women younger than menopause, the risk of developing cervical cancer is double for women.
The risk of developing childhood cancers often increases with the age of a person. Cancer of the lungs, esophagus, kidney, liver, and stomach often occurs later in life than cancer of other parts of the body. Men are more likely to suffer from cancer of the larynx, trachea, vocal cords, and pancreas. The risk of experiencing adolescent cancers is more likely to occur among black men and Native Americans.
As of now, there is no way to predict how long someone will live. It is impossible to tell if an individual will live for five years, ten years, or twenty years. However, some types of cancer often respond well to treatments, while others tend to respond poorly. Research has shown that some types of cancer tend to have higher survival rates than other types. Since the prognosis for all types of childhood cancers is unknown at this time, researchers are working hard to find better ways to treat different types of childhood cancers.
Some types of childhood cancers tend to be relatively easy to treat, such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. These cancers do not usually have very severe symptoms. However, some types of these cancers tend to spread throughout the body and kill surrounding healthy cells, sometimes resulting in cancerous tumors. Research has been investigating new treatment methods for many types of childhood cancers, to find methods of prevention.
Research has also focused on looking at how to prevent cancer in order to improve the quality of life for older adults. Most common cancers occur in younger adults, and some rarer cancers occur in older adults as well. Prevention methods include avoiding sun exposure, wearing sunscreen and quitting smoking. Researchers are currently researching prevention methods such as immunotherapy, which uses immune system boosting to target cancer cells.
Oren Zarif – Psychokinesis Treatment