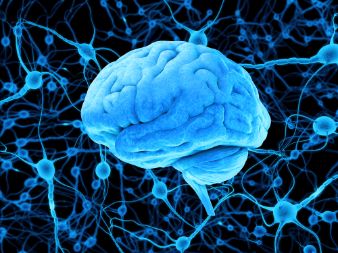
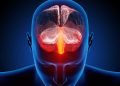
Stroke Symptoms can be hard to recognize at first, and they may even go unnoticed by some individuals. A lot of individuals think that strokes are not as deadly as other types of the vascular illnesses and diseases, like heart attacks and angina. Stroke Symptoms can be categorized into three, which are namely, hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke and transverse hemorrhagic stroke. Let us have a look on each of them.
Hemorrhagic stroke symptoms appear when the blood flow to the brain is reduced. As a result of the lack of oxygen, brain cells die. There are many reasons for this; most of the times it happens because of hypertension, atherosclerosis, cerebral palsy or a brain tumor. When the blood clots, it forms an artificial clot, known as an ischemic stroke.
The second type of stroke symptoms is known as ischemic or also called “amygdala-like” stroke. This is due to the excessive accumulation of fatty deposits in the brain. This accumulation of fat can cause more stress to the delicate blood vessels. In addition, it can also lead to a higher risk of heart attack. When the blood clots, it forms a bump, known as a plaque, within the arterial walls. These plaques block the access of the nutrients to the brain and thus they worsen the problem.
One of the most common stroke symptoms is difficulty in breathing. It can be difficult to diagnose this symptom as it is similar to the symptoms of respiratory problems like shortness of breath. For instance, if you suddenly feel shortness of breath on one side of your body, and shortness of breath on the other side of your body, then you should check out for any sort of lung irritation. However, there are other warning signs that should guide you in contacting the emergency services. If you experience any of these symptoms on one arm or one side of your body, then you should immediately call 911 or go for an ambulance.
Another of the important stroke symptoms is called TPA or Transfusion of Protein. The technical term for this is “tissue fractionation with autologous protein”. This term describes a process by which the clots are injected into the affected area or into a blood vessel directly. This is usually done after the patient’s physician has determined that the clots are not blocking the artery or vein and thus does not need any invasive procedure. Generally, this procedure is performed if the patient has a history of allergic reactions to the local anesthesia, such as some of the local anesthetic agents like nitrous oxide and nitroglycerin, certain anesthetics like propofol and phenobarbital, and some of the local anesthetic agents like midazolam.
There are other types of stroke symptoms that you should be aware of. One of these is called vasculitis. Vasculitis is similar to the symptoms of meningitis; however, it occurs in the neck rather than in the brain. This is caused by swelling of the muscles that surround the brain. Other symptoms of vasculitis include a hard, dry cough that produces white mucus; a feeling of fullness in the throat or chest when eating; and a pain or stiffness in the neck, shoulders, arms, or back that is similar to the symptoms of a heart attack. These symptoms occur in roughly one out of every five patients who suffer a stroke, so they are pretty routine.
The third most common after-effect of strokes is called rebound depression. Patients who have just had a major stroke often experience rebound depression following their recuperation. This is a result of their brain having to deal with two major changes: a reduction in memory and concentration, and the sudden cessation of all physical and mental abilities.
The final four after-effects of stroke are not usually life-threatening. One is called hyponatremia and can occur in up to thirty percent of patients who have had hemorrhagic or ischemic strokes. It is caused by the loss of muscle bulk and the increase in water within the body. Another symptom is weakness or numbness in the face, extremities, or legs. And last but not least, a feeling of depression or hopelessness is experienced by many patients who have not yet fully recovered from their stroke.
Oren Zarif – Psychokinesis Treatment